A weak or inconsistent bag closure is more than an inconvenience—it’s a direct threat to your product integrity, operational efficiency, and bottom line. When product spillage, maintenance headaches, and integration challenges disrupt your workflow, the source is often the most critical component on your line: the bag sewing machine. Understanding this equipment is the first step toward achieving the reliability and high performance you demand.
This guide provides that clarity. We break down the core mechanics, identify critical components, and explain the differences between stitch types so you can make informed decisions. You will learn how to properly maintain your equipment to maximize uptime and discover the principles of integrating a sewing head with your existing conveyor for a seamless, automated process. Our goal is to empower you to create a strong, consistent, and sift-proof seal on every bag, transforming your bag closing system from a source of frustration into an asset of unmatched dependability.
The Core Function of a Bag Sewing Machine in a Production Line
At its core, an industrial bag sewing machine, also known as a bag stitching machine, performs one critical function: creating a strong, reliable, and secure closure for open-mouth bags. In high-volume production environments, this final step is essential for protecting the product, ensuring safe transport, and maintaining package integrity. Industries from agriculture and animal feed to minerals and chemicals depend on the unmatched speed and durability of a sewn closure to handle heavy, abrasive, or fine materials without failure.
To see the efficiency of this equipment firsthand, the following video demonstrates a bag closing machine in action:
Why Choose Sewing Over Other Sealing Methods?
While methods like heat sealing or gluing have their place, sewing remains the superior choice for many demanding industrial applications. The key advantages are rooted in performance and reliability:
-
Unmatched Strength: A sewn closure provides superior durability and resistance to bursting, which is critical for heavy bags over 50 lbs. Unlike their domestic counterparts, specialized industrial sewing machines are engineered for high-speed, repetitive tasks on thick materials like woven polypropylene or multi-wall paper.
-
Breathability: Certain products, such as agricultural seeds or freshly milled flour, require packaging that allows air to escape. A sewn closure provides this necessary aeration, preventing bag rupture and preserving product quality.
-
Performance in Dusty Environments: Dust and fine product residue can compromise the effectiveness of heat seals and adhesives. Sewing machines are unaffected by these contaminants, ensuring a consistently secure closure every time.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Industrial sewing thread is an economical and readily available consumable, often providing a lower cost-per-bag than specialized glues or the high energy consumption of heat sealers.
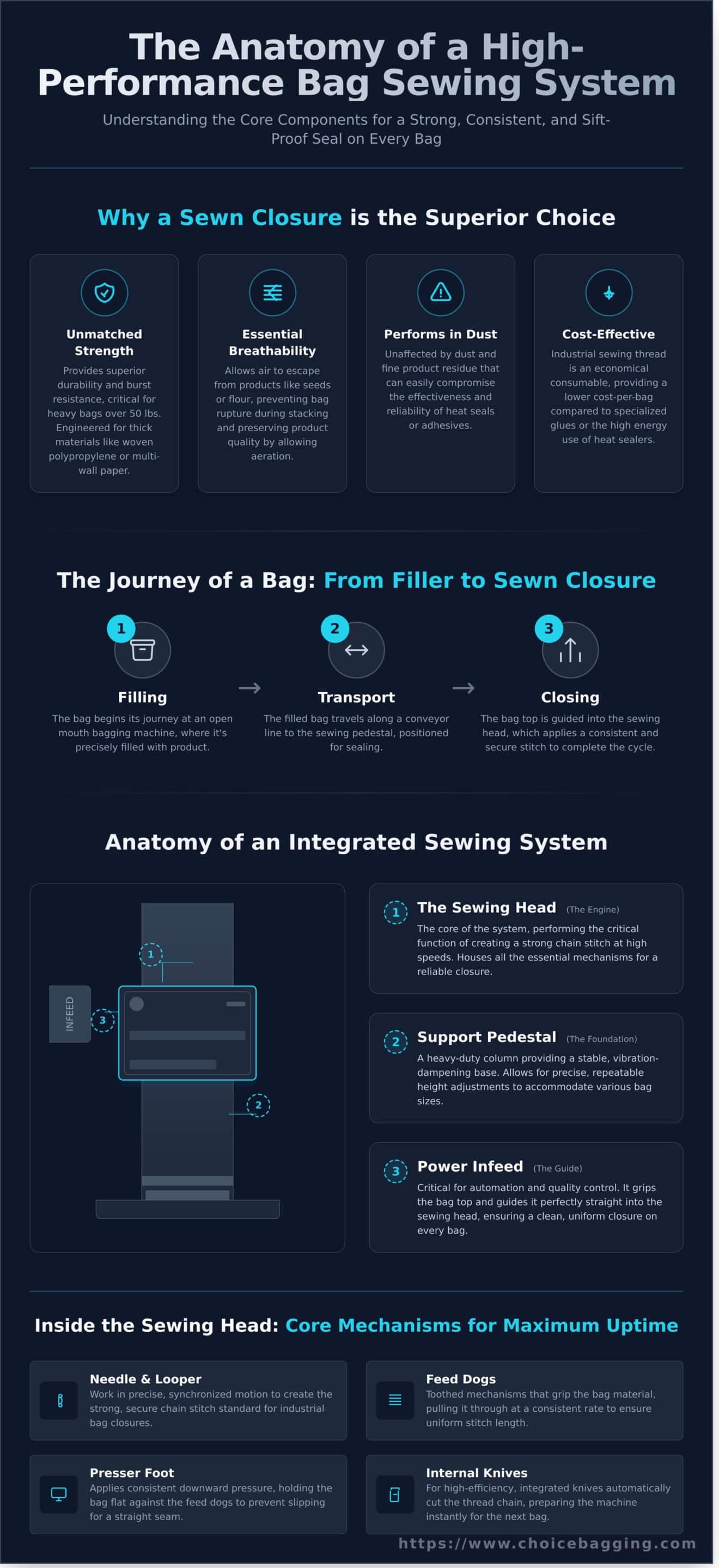
The Journey of a Bag: From Filler to Sewn Closure
The sewing head is the final, essential checkpoint in a streamlined bagging process. A bag begins its journey at an open mouth bagging machine, where it is precisely filled with product. From there, it travels along a conveyor to the sewing pedestal. As the bag top is guided into the machine, it applies a consistent and secure stitch, completing the packaging cycle with proven efficiency and reliability.
Anatomy of an Industrial Bag Sewing System: Key Components
Understanding a high-performance bag sewing machine requires looking beyond the sewing head itself. A truly efficient and reliable setup is an integrated system designed for durability and precision. This system is composed of three core elements working in unison: the sewing head, the support pedestal, and the power infeed. Each component is engineered to deliver consistent performance in demanding industrial environments.
The sewing head acts as the engine, performing the critical function of creating the stitch. However, its performance is directly dependent on the stability and guidance provided by the support structure. Let’s break down the essential parts of this complete system.
Inside the Sewing Head
The sewing head contains the core mechanisms responsible for forming a secure stitch at high speeds. Its internal components are built for minimal maintenance and maximum uptime. Key parts include:
-
Needle and Looper: These two components work together in a precise, synchronized motion to create a strong chain stitch, which is the standard for secure bag closures.
-
Feed Dogs: Located beneath the presser foot, these toothed mechanisms grip the bag material and pull it through the machine at a consistent rate, ensuring uniform stitch length.
-
Presser Foot: This applies consistent downward pressure on the bag material, holding it flat and secure against the feed dogs to prevent slipping and ensure a straight, even seam.
-
Internal Knives: For high-efficiency operations, integrated knives automatically cut the thread chain after the bag has passed, preparing the machine instantly for the next bag.
The Support System: Pedestal and Infeed
The support system provides the stable foundation and automated guidance necessary for flawless operation. A robust pedestal and a precise infeed device transform a standalone sewing head into a production powerhouse.
-
Sewing Pedestal: This heavy-duty column provides a stable, vibration-dampening base for the sewing head. Its primary function is to allow for precise, repeatable height adjustments to accommodate various bag sizes, from small pouches to large bulk bags.
-
Power Infeed: A power infeed device is critical for automation and quality control. It grips the bag top and guides it perfectly straight into the sewing head. This feature simplifies the duties of a sewing machine operator and guarantees a clean, uniform closure on every bag.
-
Variable Speed Control: To ensure seamless integration, the system must match the speed of your existing conveyor line. Variable speed controls allow for precise synchronization, preventing bag pulling or bunching and maintaining consistent production flow.
The Sewing Process Step-by-Step: From Open Bag to Secure Seal
A high-performance industrial bag sewing machine transforms a simple filled bag into a secure, ready-to-ship product in seconds. This automated sequence is a model of mechanical efficiency, engineered for reliability and consistent performance. The entire process is designed to operate with minimal human intervention, adhering to strict industrial sewing machine safety standards to protect operators while maximizing throughput. Understanding this step-by-step process is key to appreciating the value it brings to your packaging line.
Step 1: Bag Presentation and Infeed
The process begins as a filled, open-mouth bag travels along a bag handling conveyor. As it approaches the sewing station, the bag top is conditioned—flattened and reformed by guides—to ensure it is presented at the correct height and angle. A photo-eye sensor detects the bag’s leading edge, triggering the sewing cycle. The infeed device then takes control, securely gripping the bag top and feeding it into the sewing head at a consistent, controlled speed for a perfectly straight closure.
Step 2: Stitch Formation
Once inside the sewing head, the critical action of stitch formation occurs. This is a high-speed, synchronized mechanical process:
-
The needle, carrying the thread, pierces through all layers of the bag material.
-
As the needle reaches its lowest point, a component called a looper moves in a precise arc, catching the loop of thread from the needle.
-
The needle retracts, and the feed dogs—small, toothed mechanisms below the bag—simultaneously pull the material forward by a set distance.
This perfectly timed sequence repeats hundreds of times per minute, creating a strong, dependable chain stitch that securely closes the bag.
Step 3: Thread Cutting and Release
As the newly stitched bag exits the sewing head, a second photo-eye sensor detects its trailing edge. The bag sewing machine continues to run for a moment, creating a short thread chain, or tail, past the end of the bag. This tail prevents the stitch from unraveling. Instantly, a set of high-speed, automated knives activates, cleanly cutting the thread. The now securely sealed bag is released from the infeed and continues onto an exit conveyor, ready for palletizing or shipping.
Common Stitch Types and Closure Options
Selecting the right bag closure is a critical decision that directly impacts product integrity, security, and the end-user experience. The type of stitch your industrial bag sewing machine creates is not a one-size-fits-all solution; it must be matched to your product’s specific requirements for strength, protection, and ease of opening.
Understanding the fundamental differences in stitch types ensures your packaging line operates with maximum efficiency and reliability.
Single-Thread vs. Double-Thread Stitches
The two most prevalent stitch types in industrial bagging are the single-thread (Type 101) and double-thread (Type 401) chainstitches. Each offers distinct advantages for different applications.
-
Single-Thread (Type 101): This simple stitch is formed with one continuous thread. Its primary benefit is ease of opening—the entire stitch can be unraveled by pulling the correct end. This makes it ideal for products like animal feed or seed, where the customer needs quick and easy access. While economical, it is less secure than a double-thread stitch.
-
Double-Thread (Type 401): For superior strength and security, the double-thread stitch is the industry standard. It uses two separate threads (a needle thread and a looper thread) to create a more robust, interlocking seam that resists unraveling. This closure is essential for heavy products, valuable materials, or any application where seal integrity is paramount.
Adding Protection with Crepe Tape Closure
For fine, powdered products, even a secure stitch line can allow for sifting and product loss. A crepe tape closure provides a simple yet highly effective solution. This involves feeding a strip of durable paper tape over the bag top, which is then folded and stitched through along with the bag material.
This "stitch-through-tape" method creates a sift-proof seal that is essential for packaging products like flour, cement, sugar, and fine chemicals. The crepe tape completely covers the needle holes, preventing leakage and protecting the contents from moisture and contamination. Most high-performance bag sewing machine models can be equipped with folders and cutters to apply crepe tape automatically, ensuring consistent and efficient sealing.
For expert consultation on the best closure type for your specific application, we invite you to contact our team of specialists for a comprehensive assessment.
Maintaining Your Bag Sewing Machine for Peak Performance
In any industrial operation, unscheduled downtime is a significant drain on productivity and profitability. A high-performance bag sewing machine is an investment in your efficiency, and protecting that investment requires a commitment to routine care. At Choice Bagging Equipment, we are more than just a supplier; we are your partner in ensuring long-term reliability. Proper preventative maintenance is the single most effective way to extend the life of your equipment and guarantee consistent, high-quality bag closures for years to come.
By following a simple, structured maintenance schedule, you can prevent most common issues before they lead to a full shutdown, ensuring your packaging line operates at peak performance.
Essential Preventative Maintenance Tasks
A proactive approach to maintenance is fundamental. Integrating these simple tasks into your weekly workflow will dramatically improve machine durability and reduce unexpected failures.
-
Daily Cleaning: Dust, thread clippings, and product residue can accumulate quickly, interfering with moving parts. Use compressed air to clean the feed dogs, loopers, and needle area at the end of each shift.
-
Regular Oiling: Proper lubrication is critical to prevent premature wear. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for oiling points and frequency, using only the recommended type of oil.
-
Weekly Inspections: Carefully inspect key components for signs of wear or damage. Check that needles are sharp and straight, and examine loopers and knives for dullness or nicks that could cause thread breakage.
-
System Checks: Verify that thread tension is set correctly for your application and that the feed dog timing is accurate to ensure uniform stitch length.
Troubleshooting Common Sewing Issues
Even a well-maintained bag sewing machine can experience occasional issues. Here are solutions to the most common problems:
-
Skipped Stitches: This is often caused by a dull, bent, or incorrectly installed needle. It can also indicate an issue with the machine’s timing.
-
Thread Breakage: Check the entire thread path for burrs or sharp edges. Ensure the machine is threaded correctly and that the tension is not too tight.
-
Uneven Stitches: This typically points to an issue with the presser foot pressure or a problem with the feed dogs not gripping the bag material properly.
While this guidance can resolve minor problems, complex mechanical or timing issues require professional expertise. For persistent problems that disrupt your operation, trust our expert field service technicians to provide dependable, on-site support. Our commitment is to keep your equipment running reliably. Contact us today to learn more about our support services.
Secure Your Throughput with a High-Performance Bag Sewing System
Understanding the intricate mechanics of an industrial bag sewing system—from its core components to the precise sewing process—is the first step toward optimizing your packaging line. As we have covered, consistent performance hinges not just on the machine’s initial setup but on diligent maintenance and selecting the correct closure for your product. This knowledge empowers you to minimize downtime and maximize output, ensuring every bag is sealed with professional-grade security.
However, knowing how a machine works is only half the battle. Partnering with an expert ensures your equipment is seamlessly integrated and built to last. A high-quality bag sewing machine is a critical investment in your operational reliability.
Since 1978, Choice Bagging Equipment has been that partner for countless operations. We provide reliable, heavy-duty equipment Made in the USA, backed by expert integration support and comprehensive parts and service programs. When you are ready to invest in unmatched durability and performance, we are here to help.
Take the next step toward a more efficient and dependable production line. Explore Our Reliable Bag Sewing Machine Systems and discover how our commitment to quality can secure your success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a bag sewing machine and a portable bag closer?
An industrial bag sewing machine is a fixed sewing head, typically mounted on a pedestal and integrated into an automated or semi-automated bagging line. It is engineered for high-volume, continuous operation and maximum efficiency. In contrast, a portable bag closer is a handheld device designed for lower-volume applications, repairs, or situations where mobility is essential. While both perform the same core function, the fixed machine offers superior speed, consistency, and durability for demanding production environments.
How fast can an industrial bag sewing machine operate?
The operational speed of an industrial sewing head is a critical factor in production efficiency. High-performance models can operate at speeds up to 2,600 stitches per minute, closing between 20 to 25 bags per minute depending on bag width and conveyor speed. This level of performance ensures that the sewing process does not become a bottleneck in your packaging line, allowing you to meet demanding output targets with unmatched reliability and consistency.
What type of thread is used for industrial bag sewing?
The standard for industrial bag sewing is high-strength, spun polyester thread. This material is chosen for its exceptional durability, resistance to abrasion, moisture, and UV degradation, ensuring a secure closure that withstands handling and shipping. The thread is typically supplied on large cones, such as 8-ounce or 5-pound spools, to support continuous, high-volume operation with minimal downtime for changeovers. We can help you select the ideal thread for your specific application.
Can you use a bag sewing machine on plastic (poly) bags?
Yes, a modern bag sewing machine is highly effective for closing certain types of plastic bags, particularly woven polypropylene (poly) bags used for products like feed, seed, and minerals. For a secure closure on these materials, it is crucial to use the correct needle type and thread, along with proper machine tension settings. This ensures a strong stitch that won’t tear the material, providing a durable and reliable seal for your product.
How often should you change the needle in a bag sewing machine?
For optimal performance and to prevent issues like skipped stitches or material damage, we recommend changing the needle after every 8 to 10 hours of continuous operation. A worn or blunt needle can compromise stitch quality and put unnecessary strain on the machine’s components. Regular needle replacement is a simple, cost-effective maintenance step that ensures consistent, high-quality bag closures and protects your investment in your equipment’s long-term reliability and performance.
What is the typical lifespan of an industrial sewing head?
A high-quality, American-made industrial sewing head is engineered for exceptional longevity. With proper routine maintenance, including regular oiling and replacement of wear parts, these robust machines are built to last for decades in demanding industrial environments. Investing in a durable bag sewing machine from a trusted manufacturer ensures you receive a reliable asset that delivers a strong return through years of consistent, uninterrupted performance in your packaging line.


Recent Comments